The amount of sunshine that hits the surface of the earth in an hour and a half is enough to power the whole world for a whole year. Solar technologies use either photovoltaic (PV) panels or mirrors that direct the sun’s rays to turn sunlight into electricity. This energy can be used to make electricity or saved in batteries or thermal storage.
Below, you’ll find links to tools and information about the basics of solar radiation, photovoltaic and concentrating solar-thermal power technologies, integrating electrical grid systems, and the “soft costs” of solar energy, which are the costs that don’t involve hardware. You can also find out more about how to use solar energy and the business of solar energy. You can also learn more about solar energy and how the U.S. Department of Energy’s Solar Energy Technologies Office drives new study and development in these areas. How does solar power work? Continue reading for details.
What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is a renewable and safe form of energy that uses the sun’s rays to make electricity or heat. It is a clean and plentiful form of energy that has many benefits. Photovoltaic cells, which are what solar panels are, take in sunlight and turn it straight into electricity. This technology is good for the earth because it doesn’t make any harmful emissions and it cuts greenhouse gas emissions by a lot. Solar energy is a cheap and flexible option that can be used for a wide range of things, from rooftop installations in homes to large-scale solar farms. It is a key part of lowering our reliance on fossil fuels, slowing down climate change, and making the future of energy more sustainable and cleaner.
Is solar power a clean energy source?
Yes, solar power is an endless and renewable source of energy that doesn’t release any damaging greenhouse gasses. As long as the sun keeps shining, energy will be made.
Solar cells already have a small carbon footprint because they last for more than 25 years. Also, more and more of the materials used to make the panels are recovered, so the carbon footprint will keep going down.
When was solar power discovered?
People used solar energy as early as the 7th century B.C., when they used shiny items to reflect the sun’s rays and light fires. Later, in the 3rd century B.C., the Greeks and Romans used mirrors to harness the power of the sun to light candles for religious rituals.
Edmond Becquerel, a French scientist, found the photovoltaic (PV) effect in 1839, when he was only 19 years old. He did this while experimenting with a cell made of metal electrodes in a conducting solution. He noticed that the cell, which was a photovoltaic cell, made more power when it was exposed to light.
In 1954, Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller, and Gerald Pearson made the first silicon PV cell at Bell Labs. This was the first solar cell that could absorb and turn enough of the sun’s energy into electricity to run everyday electrical equipment.
Today, solar energy is used to power satellites, which are spacecraft that circle the Earth.
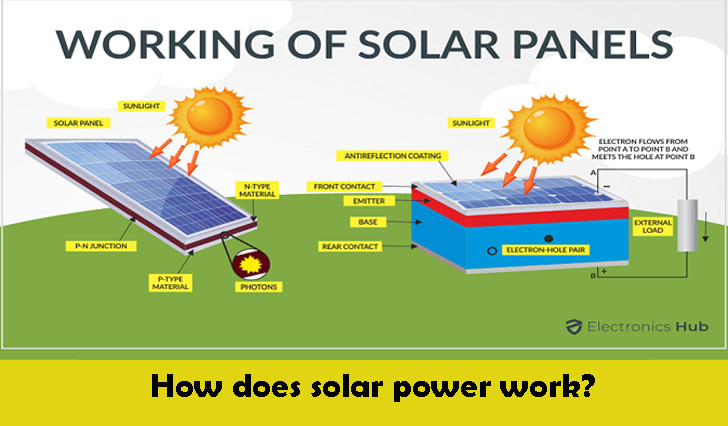
How does solar power work?
Photovoltaic cells are what make up solar panels. These cells turn the energy from the sun into power.
Between the layers of semiconducting materials like silicon are photovoltaic cells. Each layer has different electronic features that make an electric field when hit by photons from the sun. This is called the “photoelectric effect,” and it makes the electrical current that is needed to make energy.
Solar panels make power in the form of a direct current. This is then sent through a transformer, which changes it into an alternating current that can be sent to the National Grid or used by the home or business where the solar panels are installed.
How do solar panels work to generate electricity?
A standard solar panel, which is also called a solar module, is made up of a layer of silicon cells, a metal frame, a glass cover, and different wires that connect the silicon cells and allow current to run from them. Silicon is atomic number 14 on the periodic table. It is a nonmetal that can receive light and turn it into electricity because it is conductive. When light hits a silicon cell, it moves electrons, which starts an electric current. This is called the “photovoltaic effect,” and it is a good way to explain how solar panel technology works in general.
As stated above, the general way that photovoltaics work is as follows:
- Sunlight is taken in by the silicon photovoltaic solar cell.
- When the sun’s rays hit the silicon cell, electrons start to move, which makes an electric current run.
- This direct current (DC) electricity is collected by wires and sent to a solar inverter to be turned into alternating current (AC) energy.
What are some of the advantages of solar energy?
Solar electricity has a lot of benefits:
Clean and reusable: Solar power is a clean, reusable source of energy that doesn’t release greenhouse gasses or other pollutants into the air. This helps fight climate change and cleans the air.
Abundant: The sun is an almost endless source of energy that gives us a steady and large amount of energy.
Less Money Spent on energy: Installing solar panels can help you save a lot of money on your energy bill by letting you make your own electricity.
Low Operating Costs: Solar systems are easy to use and don’t cost much to run or maintain. Most of the costs come from cleaning and small repairs.
Energy Independence: People and companies can use less electricity from the grid and fossil fuels when they use solar power. This gives them more energy independence.
Creating Jobs: The solar industry provides jobs in installation, production, and repair, which helps the economy grow.
Stability of the grid: Distributed solar power can make the grid more stable and lower the chance of blackouts by using more than one source of energy.
Remote Power Generation: Solar panels can be used to make energy in remote or “off-grid” places. This makes it easier for people all over the world to get electricity.
Longevity: Solar panels usually last at least 25 years and sometimes even longer, and they often come with warranties.
Environmental Benefits: Solar energy lowers the need for fossil fuels, which are bad for the environment, and makes the air and water cleaner.
Technological Improvements: Research and development are always making solar technology better and more affordable.
Energy Storage: Advances in energy storage technology make it possible to store extra energy from the sun so that it can be used at night or on cloudy days.
Because of these benefits, solar energy is becoming a more popular and sustainable way to get energy for both homes and businesses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, photovoltaic cells or solar panels collect sunshine and turn it into electricity. This process is clean, renewable, and good for the environment. It has many benefits, such as lowering your energy bill and fighting climate change. As technology improves and makes solar power easier to use, it will continue to be a key part of making sure that our planet’s energy future is cleaner and more viable.